Let’s say you are connected to an Azure SQL server, and you want to make a query to compare the content of two tables on different servers (for instance, to compare the data after a migration).
This is how you can do it.
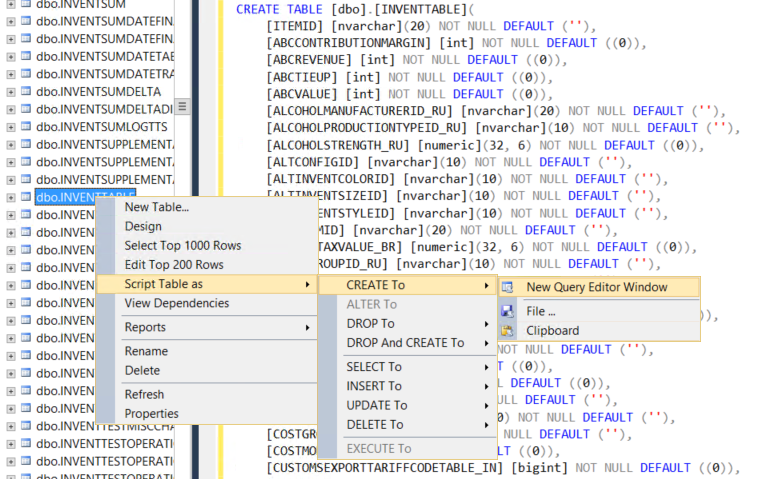
First step : prepare the remote table definition
Connect to the remote database, and generate the table definition. You may remove the unnecessary columns. Do not copy the index or primary key part, just the table and column part.
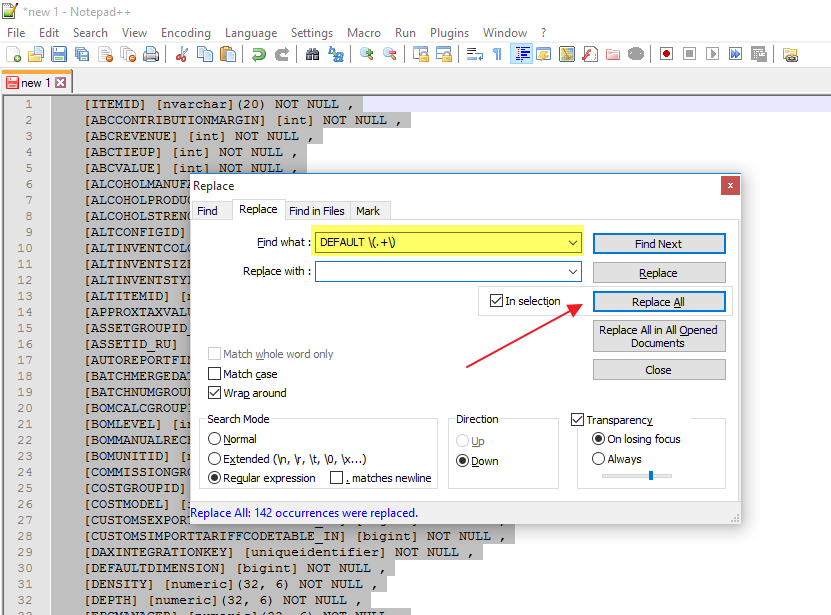
In Notepad++ (or any other text editor with regexp capabilities), remove the “DEFAULT” constraints :
Second step : create the remote table reference
Now, connect to the server from which you want to query, prepare and run the following script :
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'P#rj5++yFIjAy##*'; -- random CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL AxSqlCredentials WITH IDENTITY = 'sqladmin', SECRET = 'e*XXXXXIBmz'; -- the password CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE RemoteReferenceData WITH ( TYPE=RDBMS, LOCATION='fxdhcgvhjssf.database.windows.net', DATABASE_NAME='axdb_0abhjgjvgjfz1108', CREDENTIAL= AxSqlCredentials ); CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[InventTable]( [ITEMID] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL , [ABCCONTRIBUTIONMARGIN] [int] NOT NULL , [ABCREVENUE] [int] NOT NULL , ... [CREATEDBY] [nvarchar](20) NOT NULL ) WITH ( DATA_SOURCE = RemoteReferenceData );
Now that the reference to the table is ready, you can query the table as if it was local :
select * from dbo.InventTable
This technique can be used to distribute heavy processing accross serveral SQL servers.